LiDAR is the acronym for “Light Detection And Ranging”, sometimes called 3D laser scanning. It is like a RADAR that works with light instead of sound. This technology was first used in 1961 shortly after the invention of the laser. In recent years the invention of Autonomous vehicles and drones has increased the demand for this technology.
Flash LiDAR
In flash LiDAR, the technology illuminates the entire field of view with a wide diverging laser beam in a single pulse. This kind of technology is different from conventional scanning where the camera illuminates one point at a time, and the beam is scanned point by point. In both cases, scanning and flash LiDAR uses the time that took the light to come back and then determines the distance between the sensor and the object. In other words, Flash LiDAR takes distance photos, and this device is advantageous compared to scanner LiDAR when the camera, scene or both are moving.
Once the signal (light) is received by the scanner, a series of algorithms produce a nearly instantaneous 3-D rendering of objects and terrain features within the field of view of the object.
This technology is used widely in many fields. It is used in satellites and airplanes to scan terrains and to make bathymetrics of the ocean. In agriculture is used to determine yield production in each area from the land, it can be used also to find where weed is growing and if there are insects, witch kind of insects are there and the sex of the insects.
In archeology is used to find places and sites that are not visible under naked eye, because they are covered by vegetation. Using LiDAR technology, in 2018 archeologists discovered more than 60,000 man-made structures in the Maya Biosphere Reserve.
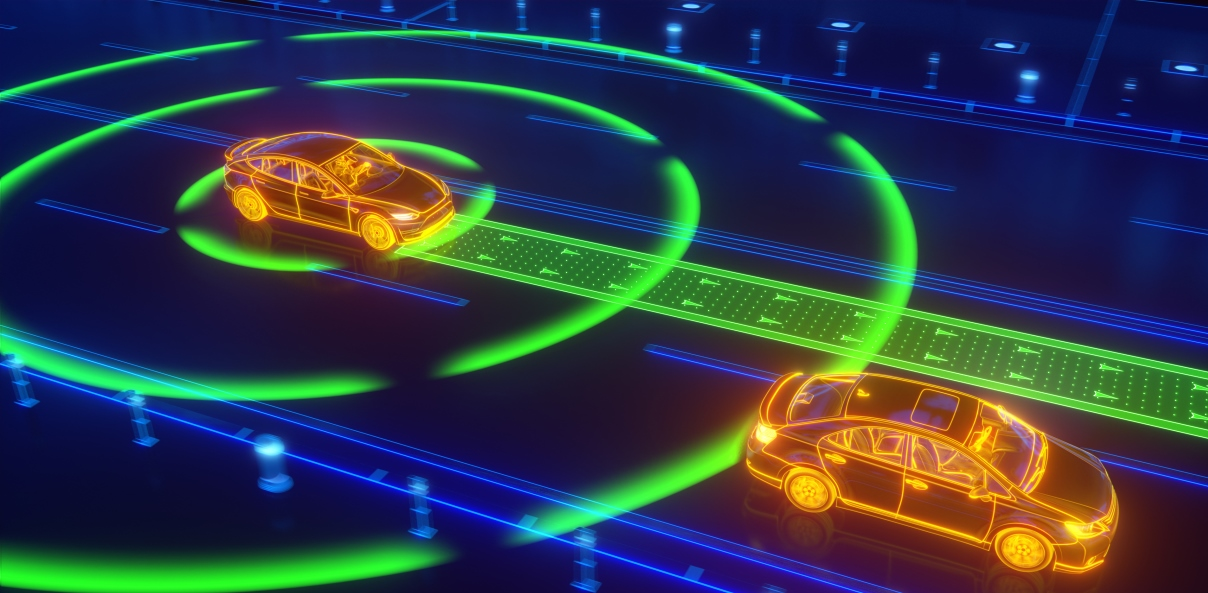
This is the form where most humans are going to interact, even if users have no knowledge about the existence of this technology. Self driving cars or autonomous vehicles are the vehicles designed and produced by several companies that have the ability to drive by themselves using advanced control systems and sensors to identify appropriate navigation paths. Self driving cars may use LiDAR technology to find obstacles and avoid them, navigating safely through environments.
Also LiDAR is used in:
- Biology and conservation
- Geology and soil science
- Atmosphere
- Law enforcement (speed guns and crime scene scanning)
- Military
- Mining
- Physics and astronomy
- Rock mechanics
- Robotics
- Spaceflight
- Surveying
- Transport
- Wind farm optimization
- Solar photovoltaic deployment optimization
- Video games
The LiDAR market size is expected to grow up to USD 2.8 billion by 2025 from an estimated size of USD 1.1 billion in 2020, at a CAGR of 20.7% from 2020 to 2025. The rising adoption of LiDAR systems in Autonomous Vehicles, increasing adoption of LiDAR in different fields as construction applications and engineering, the use of LiDAR in geographical information systems (GIS), the emergence of 4D LiDAR company, and improving the regulations related to use of commercial drones in different applications are some of the factors thriving the growth of the LiDAR market.